Tooth pain can range from a mild discomfort to severe throbbing sensations, often signaling underlying dental issues that require attention.
Understanding the signs and symptoms of serious tooth pain is crucial for timely intervention and proper dental care.
Tooth pain is a common complaint that can arise due to various reasons.
It occurs when the nerve in the tooth’s pulp becomes irritated, often indicating an underlying dental problem.
Different types of tooth pain can indicate different issues, ranging from minor concerns to serious conditions that require immediate attention.
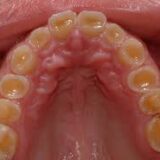
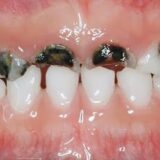
One of the primary causes of tooth pain is dental cavities (caries) resulting from bacterial decay of the tooth enamel and dentin.
Cavities can lead to sensitivity and discomfort, especially when eating or drinking.
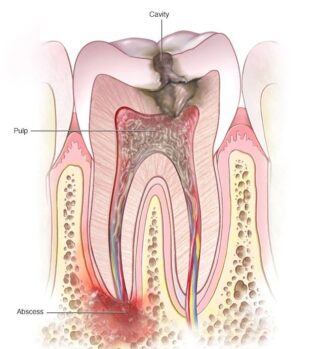
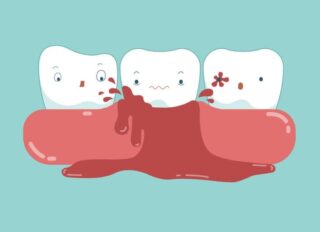
Periodontal issues like gingivitis or periodontitis can cause tooth pain due to inflammation and infection of the gums, leading to gum recession and exposure of sensitive tooth roots.
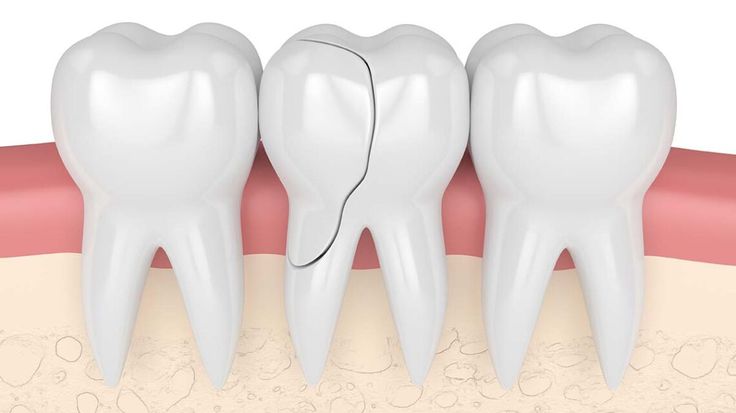
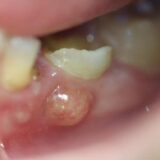
A cracked or fractured tooth can cause sharp pain, particularly when biting down or consuming hot or cold substances.
Exposed tooth roots due to receding gums or enamel erosion can result in heightened sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods.

Certain signs accompanying tooth pain may indicate a more serious underlying dental condition:
Persistent Pain: Continuous or worsening pain not relieved by over-the-counter medications.
Swelling and Redness: Inflammation around the tooth or gums, often accompanied by tenderness.
Prolonged Sensitivity: Lingering sensitivity to heat, cold, or pressure.
Bad Breath or Taste: Persistent bad breath or unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Difficulty Eating or Drinking: Pain or discomfort when chewing or consuming certain foods.
It’s essential to seek professional dental care promptly under the following circumstances:
Immediate Attention: Severe, sudden pain, especially with swelling or fever.
Persistent Symptoms: Tooth pain lasting more than a few days, even if mild.
To diagnose the cause of tooth pain, a dentist may perform the following:
Dental Examination: Visual inspection of the teeth and gums.
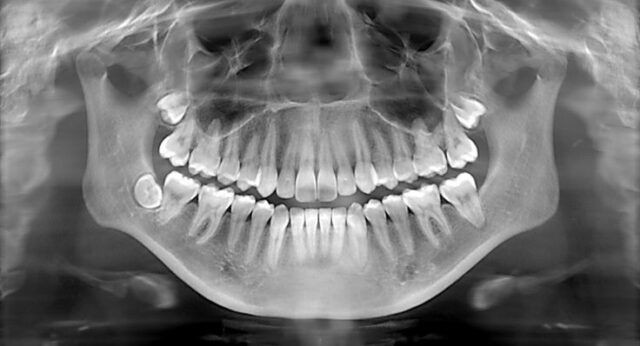
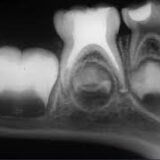
X-rays: Imaging to identify cavities, fractures, or infection.
Tests for Sensitivity: Assessing response to temperature or pressure changes.
Treatment for tooth pain depends on the underlying cause:
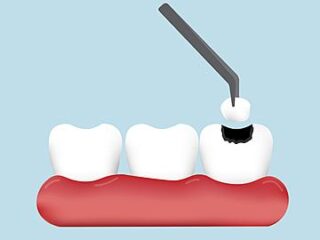
Repair cavities to restore tooth structure.
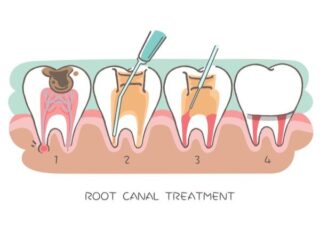
Removal of infected pulp to save the tooth

Scaling and root planning to address gum disease

Removal of severely damaged or infected teeth
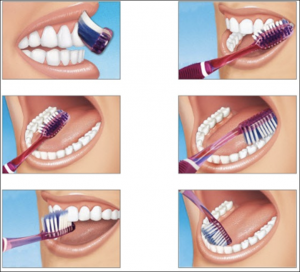

Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental visits can help prevent tooth pain and serious dental issues.
Brushing twice a day, flossing, and using mouthwash are essential habits for dental health.



While awaiting professional care, certain home remedies may provide temporary relief:
Pain Relief Medications: Over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen.
Saltwater Rinse: Gargling with warm saltwater to reduce inflammation.
Cold Compress: Applying a cold pack to the cheek outside the affected area.
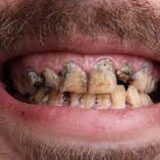
Ignoring tooth pain can lead to complications such as:
Risk of Infection: Dental infections can spread to other parts of the body.
Tooth Loss: Advanced decay or infection may necessitate tooth extraction.
Tooth pain is often a warning sign of underlying dental issues that should not be ignored.
Seeking timely dental care and adopting preventive measures are crucial for maintaining good oral health and preventing serious dental problems.
Can tooth pain go away on its own?
Tooth pain may temporarily subside, but it’s essential to address the underlying cause to prevent worsening symptoms.
What should I do if I have sudden severe tooth pain?
Seek immediate dental attention, as severe pain could indicate an acute infection or abscess.
How often should I visit the dentist for check-ups?
It’s recommended to visit the dentist every six months for routine check-ups and cleanings.
Are home remedies effective for treating tooth pain?
Home remedies can provide temporary relief, but they do not replace professional dental care.
Is tooth sensitivity always a sign of a serious problem?
Not necessarily, but persistent sensitivity should be evaluated by a dentist to rule out underlying issues.




Tooth pain can range from a mild discomfort to severe throbbing sensations, often signaling underlying dental issues that require attention.
Understanding the signs and symptoms of serious tooth pain is crucial for timely intervention and proper dental care.
Tooth pain is a common complaint that can arise due to various reasons.
It occurs when the nerve in the tooth’s pulp becomes irritated, often indicating an underlying dental problem.
Different types of tooth pain can indicate different issues, ranging from minor concerns to serious conditions that require immediate attention.
One of the primary causes of tooth pain is dental cavities (caries) resulting from bacterial decay of the tooth enamel and dentin.
Cavities can lead to sensitivity and discomfort, especially when eating or drinking.

Periodontal issues like gingivitis or periodontitis can cause tooth pain due to inflammation and infection of the gums, leading to gum recession and exposure of sensitive tooth roots.

A cracked or fractured tooth can cause sharp pain, particularly when biting down or consuming hot or cold substances.

Exposed tooth roots due to receding gums or enamel erosion can result in heightened sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods.

Certain signs accompanying tooth pain may indicate a more serious underlying dental condition:
Persistent Pain: Continuous or worsening pain not relieved by over-the-counter medications.
Swelling and Redness: Inflammation around the tooth or gums, often accompanied by tenderness.
Prolonged Sensitivity: Lingering sensitivity to heat, cold, or pressure.
Bad Breath or Taste: Persistent bad breath or unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Difficulty Eating or Drinking: Pain or discomfort when chewing or consuming certain foods.
It’s essential to seek professional dental care promptly under the following circumstances:
Immediate Attention: Severe, sudden pain, especially with swelling or fever.
Persistent Symptoms: Tooth pain lasting more than a few days, even if mild.
To diagnose the cause of tooth pain, a dentist may perform the following:
Dental Examination: Visual inspection of the teeth and gums.

X-rays: Imaging to identify cavities, fractures, or infection.

Tests for Sensitivity: Assessing response to temperature or pressure changes.
Treatment for tooth pain depends on the underlying cause:

Repair cavities to restore tooth structure.

Removal of infected pulp to save the tooth

Scaling and root planning to address gum disease

Removal of severely damaged or infected teeth



Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental visits can help prevent tooth pain and serious dental issues.
Brushing twice a day, flossing, and using mouthwash are essential habits for dental health.



While awaiting professional care, certain home remedies may provide temporary relief:
Pain Relief Medications: Over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen.
Saltwater Rinse: Gargling with warm saltwater to reduce inflammation.
Cold Compress: Applying a cold pack to the cheek outside the affected area.
Ignoring tooth pain can lead to complications such as:
Risk of Infection: Dental infections can spread to other parts of the body.
Tooth Loss: Advanced decay or infection may necessitate tooth extraction.
Tooth pain is often a warning sign of underlying dental issues that should not be ignored.
Seeking timely dental care and adopting preventive measures are crucial for maintaining good oral health and preventing serious dental problems.
Can tooth pain go away on its own?
Tooth pain may temporarily subside, but it’s essential to address the underlying cause to prevent worsening symptoms.
What should I do if I have sudden severe tooth pain?
Seek immediate dental attention, as severe pain could indicate an acute infection or abscess.
How often should I visit the dentist for check-ups?
It’s recommended to visit the dentist every six months for routine check-ups and cleanings.
Are home remedies effective for treating tooth pain?
Home remedies can provide temporary relief, but they do not replace professional dental care.
Is tooth sensitivity always a sign of a serious problem?
Not necessarily, but persistent sensitivity should be evaluated by a dentist to rule out underlying issues.