Outline of Article:
- Introduction
- What Are Gum Diseases?
- Types of Gum Diseases: Gingivitis &Periodontitis
- Causes of Gum Diseases
- – Poor Oral Hygiene
- – Smoking
- – Diabetes
- – Genetic Predisposition
- – Hormonal Changes
- – Medications
- Signs and Symptoms
- Risk Factors
- Complications of Untreated Gum Diseases
- Prevention of Gum Diseases
- – Oral Hygiene Practices
- – Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- – Regular Dental Check-ups
- Treatment Options
- – Professional Cleaning
- – Scaling and Root Planning
- – Antibiotics
- – Surgery
- Importance of Early Detection
- Conclusion
- FAQs (5 unique questions)
The shocking truth about Gum diseases : Are you at risk?
1.The Shocking Truth About Gum Diseases: Are You at Risk?
Gum diseases possess a significant threat to oral health, yet many people underestimate their severity. Understanding the risks and taking preventive measures is crucial to maintaining healthy gums and teeth.
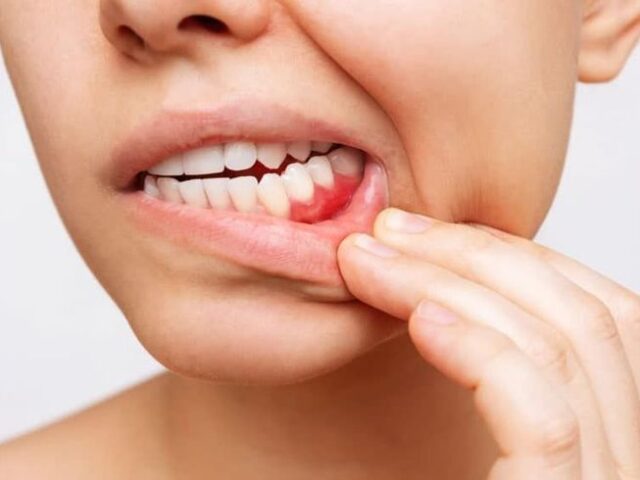
2.What Are Gum Diseases?
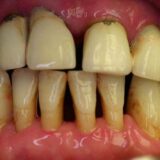
Gum diseases, also known as periodontal diseases, are bacterial infections that affect the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. These conditions range from mild inflammation to severe damage and can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
3.Types of Gum Diseases
Gingivitis:
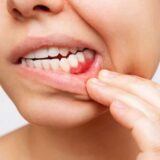
– Gingivitis is the mildest form of gum disease, characterized by red, swollen gums that bleed easily. It is often caused by poor oral hygiene and can be reversed with proper care.
Periodontitis:
– Periodontitis is a more advanced stage of gum disease, where the infection spreads to the bone and ligaments supporting the teeth. Without intervention, it can result in tooth loss and other complications.

4.Causes of Gum Diseases
Several factors contribute to the development of gum diseases:
- – Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate, leading to gum inflammation.
- – Smoking: Tobacco use weakens the immune system and makes it harder for the gums to heal.
- – Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes increases the risk of gum infections and impairs healing.
- – Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals are more susceptible to gum diseases due to genetic factors.
- – Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can increase gum sensitivity.
- – Medications: Certain medications, such as antihypertensives and anticonvulsants, can affect gum health.


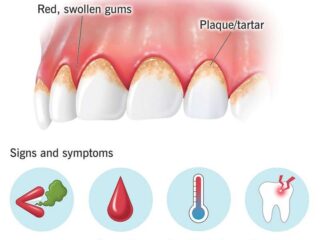
5.Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the early signs of gum disease is crucial for timely intervention:
- – Bleeding gums during brushing or flossing
- – Persistent bad breath
- – Swollen, tender gums
- – Receding gumline
- – Loose or shifting teeth
6.Risk Factors : Anyone can develop gum diseases, but some individuals are at higher risk:
- – Smokers
- – Diabetics
- – Individuals with a family history of gum disease
- – Pregnant women
- – People taking certain medications

7.Complications of Untreated Gum Diseases
Ignoring gum diseases can have serious consequences:
- – Tooth loss
- – Bone loss
- – Gum recession
- – Abscesses
- – Systemic health issues (e.g., heart disease, diabetes)
8.Prevention of Gum Diseases
Taking proactive steps to prevent gum diseases is key:
- – Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush at least twice a day, floss daily, and use mouthwash.
- – Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet, avoid tobacco products, and manage chronic conditions like diabetes.
- – Regular Dental Check-ups: Schedule routine dental visits for professional cleanings and early detection of any issues.

If gum disease develops, various treatment options are available:
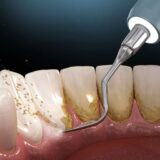
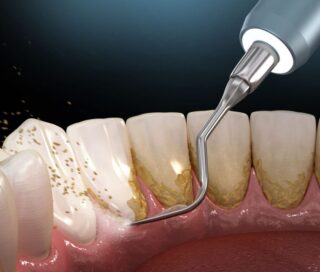
- – Professional Cleaning: Removal of plaque and tartar buildup by a dental hygienist.
- – Scaling and Root Planning: Deep cleaning to remove bacteria and smooth root surfaces.
- – Antibiotics: Oral or topical antibiotics to control bacterial infection.
- – Surgery: In severe cases, surgical procedures like flap surgery or bone grafts may be necessary.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection and intervention can prevent gum diseases from progressing and causing irreversible damage. Regular dental check-ups are essential for monitoring gum health and addressing any issues promptly.
Conclusion
Gum diseases are not to be taken lightly. Understanding the risks, recognizing the signs, and taking preventive measures are vital for maintaining optimal oral health. By prioritizing good oral hygiene, making healthy lifestyle choices, and seeking professional dental care when needed, you can protect your gums and smile for years to come.

FAQs
- How often should I visit the dentist for check-ups?
– It is generally recommended to visit the dentist every six months for routine check-ups and cleanings. However, your dentist may suggest more frequent visits based on your individual needs.
- Can gum diseases be reversed?
– Gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease, can often be reversed with proper oral hygiene and professional dental care. However, advanced stages of gum disease may require more intensive treatment to manage.
- Is gum disease contagious?
– While the bacteria that cause gum disease can be transferred through saliva, gum disease itself is not considered contagious like the common cold or flu. However, individuals living in the same household may have similar oral hygiene habits, which can affect their risk of developing gum disease.
- Are there any natural remedies for gum disease?
– While good oral hygiene practices are the cornerstone of preventing and treating gum disease, some natural remedies like oil pulling with coconut oil or using herbal mouth rinses may offer complementary benefits. However, it’s essential to consult with your dentist before trying any alternative treatments.
- Can gum disease affect my overall health?
– Yes, gum disease has been linked to various systemic health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, respiratory infections, and pregnancy complications. Taking care of your oral health is essential for your overall well-being.